Previously YAML was known as "Yet Another Markup Language" but now it is known as "YAML Ain't Markup Language".
We will figure out why YAML's name was changed but before we need to know what's a Markup Language , to begin with.
If you have ever used HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), you know that a simple HTML code would look like this:
<html>
...
<body>
<ul>
<li>Coffee</li>
<li>Tea</li>
<li>Milk</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html
They are just tags enclosed within tags. But if you observe closely, HTML is creating a child-parent relationship.

"html" is the parent of "body" and "li" are the children of "ul".
So markup language is a standard text-encoding system consisting of a set of symbols inserted in a text document to control its structure, formatting, or the relationship between its parts.
Back to our first question, why was YAML's name changed?
Well, the answer is simple! YAML Ain't Markup Language rather it is a human-readable data-serialization language and commonly used for configuration files and in applications where data is being stored or transmitted. It basically does what JSON and XML can do. YAML is primarily for data and not for documents.
(In simple words YAML is a data format, used to store and exchange data). To exchange data YAML uses a process known as Data Serialization
Data Serialization 101
Imagine that you have a bunch of data about teachers in your school and you need to share that data with your android app, web app, and a machine learning model for some analysis.
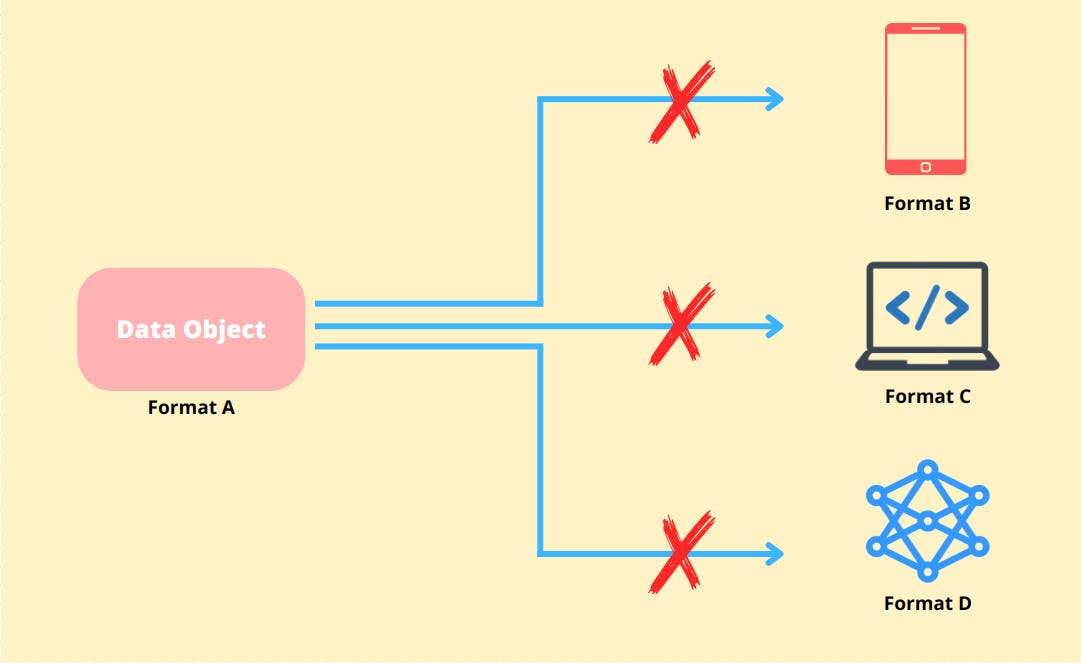
But the catch is that all of these technologies use different ways to store and handle data. So how do share data with all these different platforms?
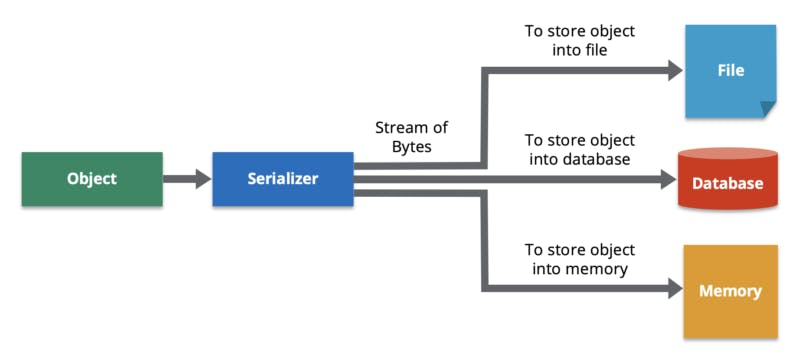
Here Data Serialization and Deserialization save your day! Basically, Data Serialization means converting your data object (data about teachers) into a stream of bytes. Then this stream of bytes is transmitted and stored.
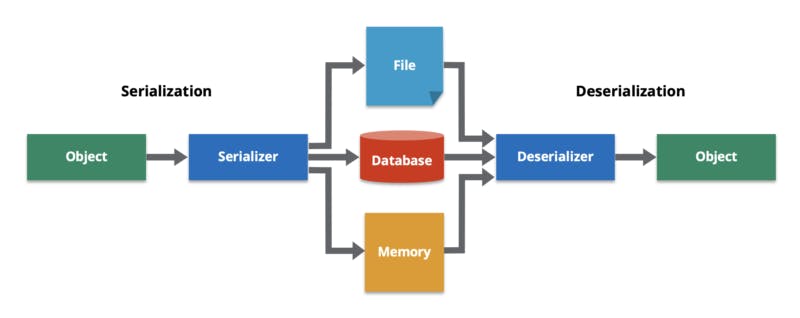
Data Deserialization is the reverse process. Converting stream of bytes back to the object.
Examples of data serialization languages:
- YAML
- JSON
- XML
In simple words, in these languages, you can store data in form of code.
Benefits of YAML?
- Simple and Easy to read
- It has strict syntax (Indentation is important)
- Easily convertible to JSON and XML
- More powerful when representing complex data
- Various tools are available for it (e.g parsers)
- Parsing is Easy
YAML Syntax
- All members of a list are lines beginning at the same indentation level starting with a
"- "(a dash and a space): [Also know as Sequence]
# A List
- Banana
- Grape
- Apple
- Orange
- All YAML files can optionally begin with --- and end with .... This is part of the YAML format and indicates the start and end of a document.
---
# A List
- Banana
- Grape
- Apple
- Orange
...
- A dictionary is represented in a simple key: value form (the colon must be followed by a space): [Aslo Known As Map]
shehzad:
name: Muhammad Shehzad
program: BSCS
semester: 3
- More complicated data structures are possible, such as lists of dictionaries, dictionaries whose values are lists, or a mix of both:
# Student records
- shehzad:
name: Muhammad Shehzad
program: BSCS
subjects:
- Data Structures and Algorithm
- Digital Logic Design
- Statistical Inference
- ali:
name: Ali Iqbal
program: BSAF
subjects:
- Finance
- Accounting
- Business
- Here is how the above YAML file would look like in JSON
// JSON
[
{
"shehzad": {
"name": "Muhammad Shehzad",
"program": "BSCS",
"subjects": [
"Data Structures and Algorithm",
"Digital Logic Design",
"Statistical Inference"
]
}
},
{
"ali": {
"name": "Ali Iqbal",
"program": "BSAF",
"subjects": [
"Finance",
"Accounting",
"Business"
]
}
}
]
You can see how much cleaner and more readable YAML is!
- Dictionaries and lists can also be represented in an abbreviated form if you really want to:
shehzad: {name: Muhammad Shehzad, program: BSCS, semester: 3}
items: ['pencil', 'eraser', 'ruler', 'pen']
- Use | if you want linebreaks to be preserved as \n
line: |
This line is split
into multiple lines
- Use > to write a single line in multiple lines
line: >
This will be all
be in a
single line
Datatypes in YAML
- Boolean.
- Numbers.
- Strings.
- Dates.
- Timestamp.
- Arrays.
- Maps.
- Null
Although these types can be inferred automatically, you can also explicitly specify them.
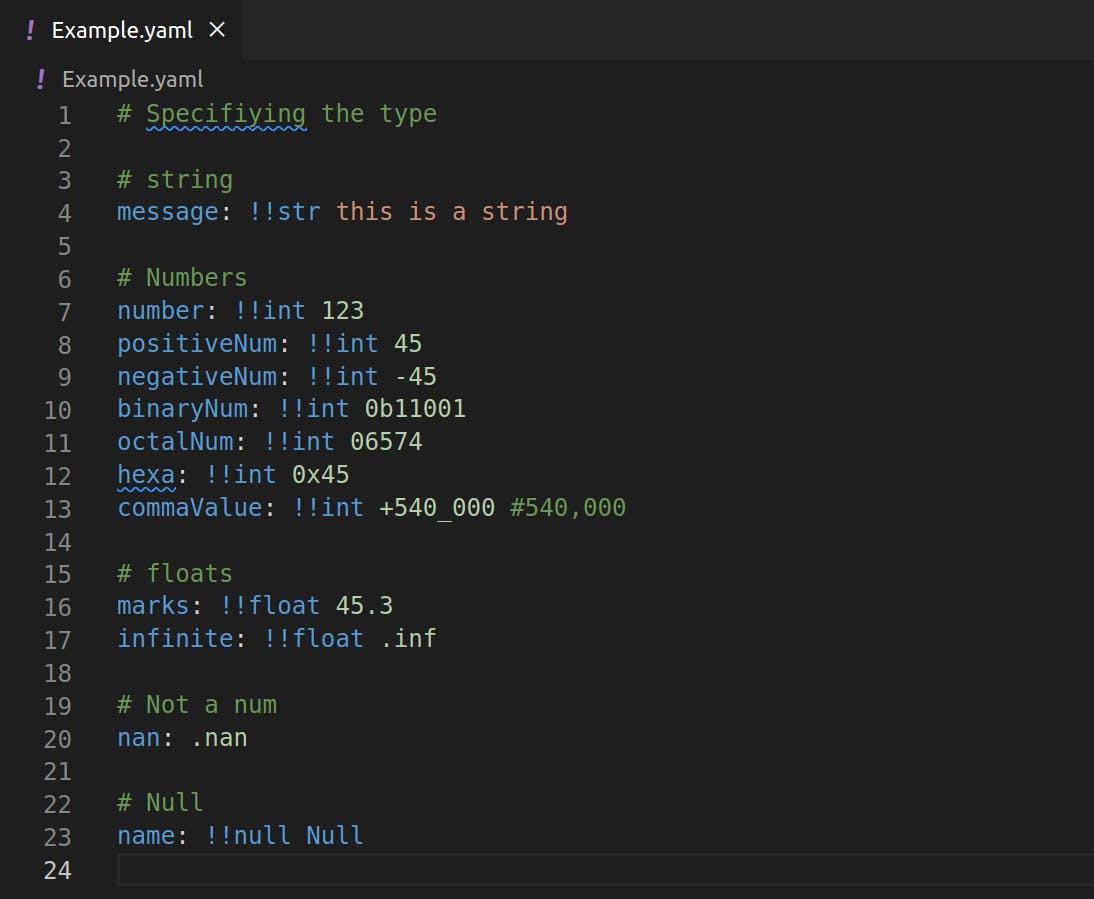
Advanced Datatypes
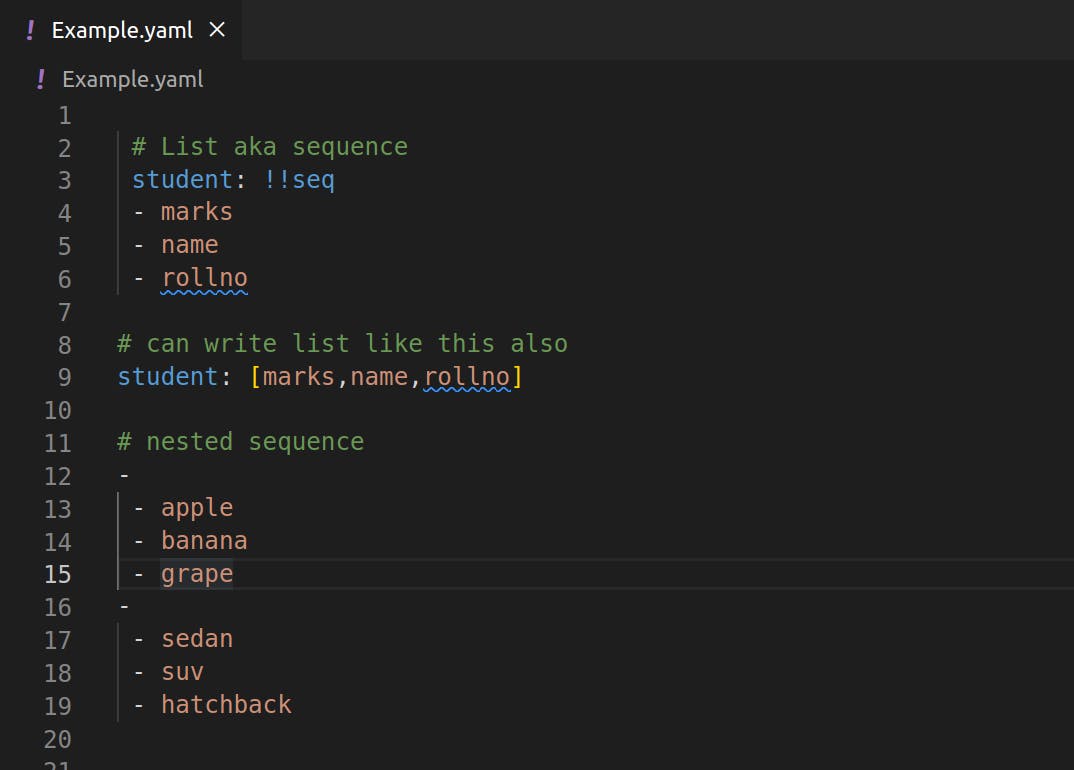
- Sequences (Lists)
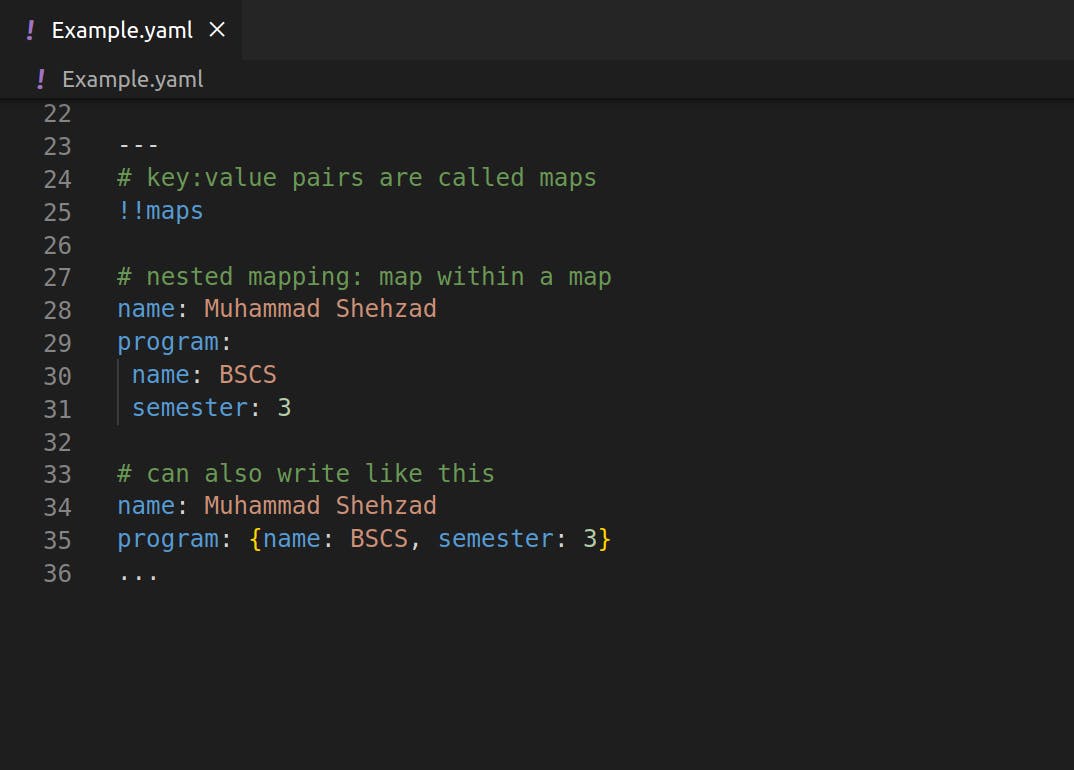
- Maps (key:value pair)
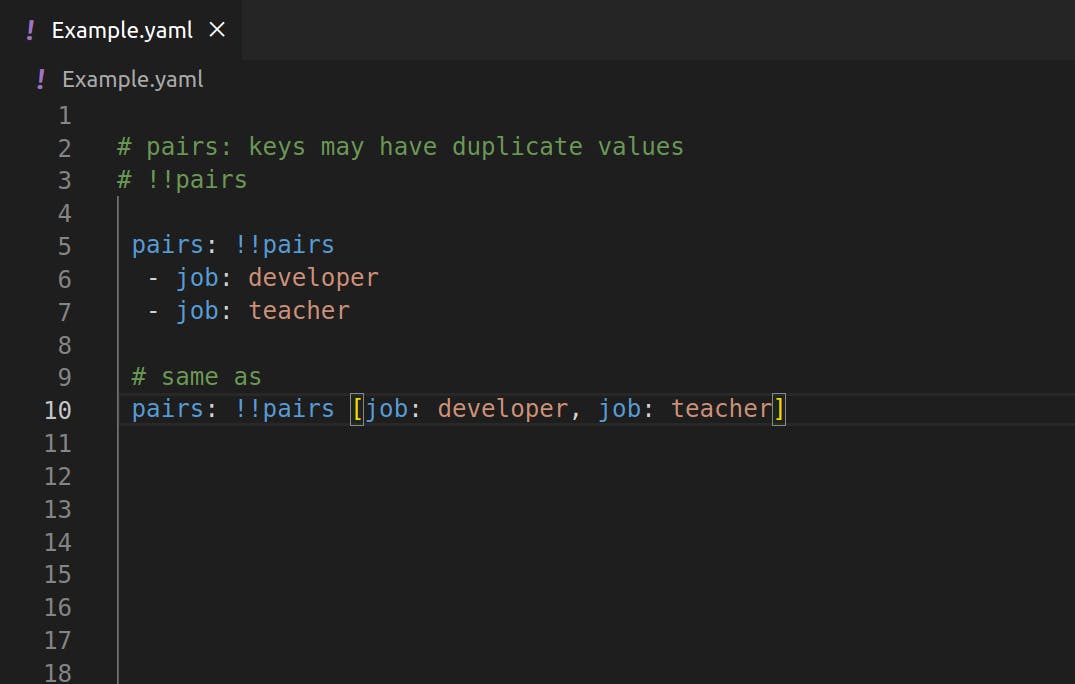
- Pairs
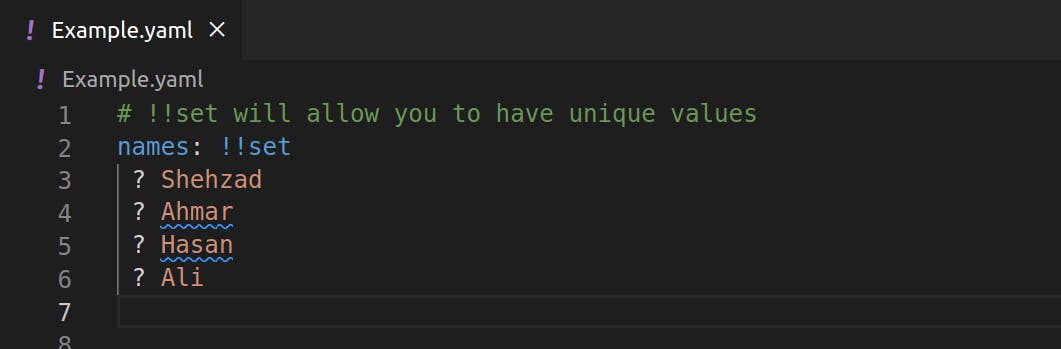
- Sets
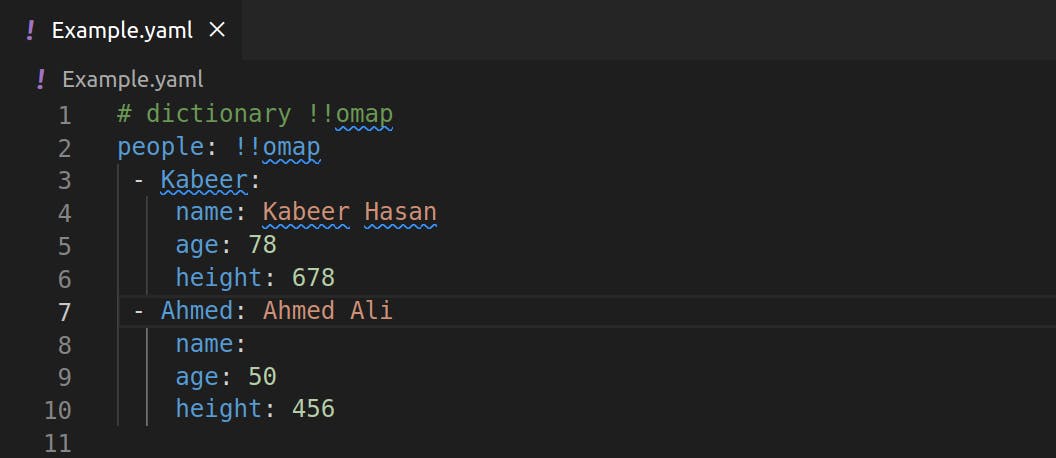
- Dictionary
YAML Tools To Make Life Easy
- YAMLlinter: Checks whether your YAML is written correctly
- datree
- Monokle
- LENS
That's pretty much it. Keep Learning!
These were my notes from Kunal Kushwaha's YAML Course. Do have a look: youtube.com/watch?v=IA90BTozdow
Muhammad Shehzad
